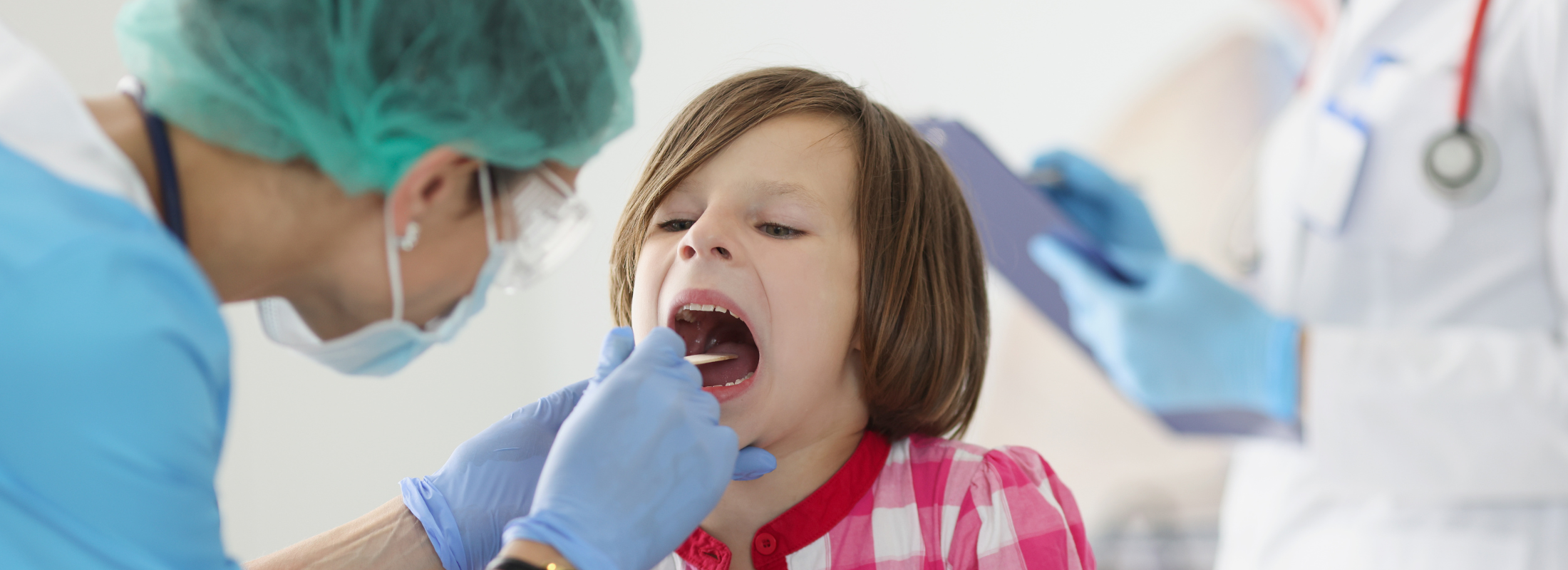
Tonsillitis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the tonsils, which are two oval-shaped pads of tissue located at the back of the throat. While tonsillitis can affect individuals of any age, it is particularly prevalent in children and adolescents.
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
The symptoms of tonsillitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common signs and symptoms may include:
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swollen, red tonsils
- White or yellow patches on the tonsils
- White dots on tonsils
- Bleeding tonsils
- Fever and chills
- Headache
- Ear pain
- Bad breath
- Hoarse voice
Causes of Tonsillitis – Is Tonsillitis Contagious?
Tonsillitis is often caused by viral or bacterial infections. Viral infections, such as the common cold or flu, are the most frequent culprits. Bacterial infections, particularly those caused by Streptococcus bacteria (strep throat), are another common cause of tonsillitis.
It’s important to note that while tonsillitis itself is contagious, not everyone who comes into contact with an infected person will develop the condition. Factors such as overall health, immune function, and personal hygiene practices can influence susceptibility to infection. Taking preventive measures such as practicing good hand hygiene and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick can help reduce the risk of contracting tonsillitis.
Prevention – How to Prevent Tonsillitis
While it may not always be possible to prevent tonsillitis entirely, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of infection:
- Practice good hand hygiene, including frequent handwashing.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick.
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tonsillitis
Diagnosing tonsillitis typically involves a physical examination of the throat and may include additional tests such as throat swabs or blood tests to determine the underlying cause, especially in cases where strep throat is suspected.
Our Urgent Care provides tonsillitis diagnosis, strep and mono rapid testing, blood analysis, and additional testing methods to help diagnose a wide variety of illnesses and ailments. If you are experiencing symptoms related to tonsillitis, visit us for a prompt diagnosis.
Treatment for tonsillitis depends on the cause and severity of the condition. In cases of viral tonsillitis, treatment is primarily focused on symptom management through rest, hydration, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Antibiotics may be prescribed for bacterial tonsillitis to help clear the infection and prevent complications. In recurrent or severe cases of tonsillitis, surgical removal of the tonsils, known as a tonsillectomy, may be recommended.